Do I Have Fallen Arches??
Overview

There are two types of flatfeet. Flexible flatfoot means that the foot has some arch, even if it only appears when the person flexes the feet or stands on the toes. This is a normal condition that is generally painless and does not require treatment. Stiff, inflexible, or painful flatfoot is an abnormal condition and may indicate a bone abnormality in the foot, a disease, or an injury. Flatfeet are a normal condition in infants and toddlers. This is partly the result of fatty deposits along the bottom of the foot that go away as the child grows. It is also because the ligaments in the foot have not fully developed. Flat-footedness in children is generally painless and does not interfere with walking or activity. In fact, as children learn to walk, the soft tissues in the foot tighten and form the arch. Most children develop arches by late childhood. When flatfeet continue into adulthood, most cases are considered normal. Incidence of flatfeet in the general population is unknown.
Causes
There are many reasons why flat feet develop. Here?s a look at some of the most common causes. Genetics, weak arches, injury, arthritis, diabetes, age, wear and tear on feet, tibialis posterior (ruptured tendon). Nervous system or muscle diseases such as cerebral palsy. Weakness and tightness of other muscles and tendons higher up in the lower extremity. The way our arches form depends on several factors. Our feet are complex structures that comprise twenty-six bones, thirty-three joints, and more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments each. Each foot forms two arches. The arch that runs from the heel to the toe is known as the longitudinal arch, while the one that runs the width is known as the transverse arch. Ligaments (fibrous tissues) give our arches their shape and hold our bones together. The plantar fascia (the long, strong band of connective tissue that runs along the sole of your foot) and muscles add secondary support. There are also foot pads that absorb impact and assist with weight-bearing functions. How these things intertwine and work together determines the formation of our arches. A structural abnormality or injury to one of these components can result in flatfoot.
Symptoms
It?s possible to have fallen arches and experience no symptoms whatsoever. But many people do notice some problems with this condition. Their feet, back and legs ache. Standing on their toes is difficult, if not impossible, and they note swelling around the arch and heel.
Diagnosis
It is important for people with foot pain to know if they have flat feet. The following tests can help you determine your arch type. When you get out of a swimming pool, look at your footprint on the concrete. The front of the foot will be joined to the heel by a strip. If your foot is flat, then the strip is the same width as the front of the foot, creating a footprint that looks like a stretched out pancake. With a normal arch, the strip is about half the width of the front of the foot. If you have a high arch, only a thin strip connects the front of the foot with the heel. Put your shoes on a flat table and view them at eye level from behind. See if the sole is worn evenly. A flat foot will cause more wear on the inside of the sole, especially in the heel area. The shoe will easily rock side to side. A flat foot will also cause the upper part of the shoe to lean inward over the sole. Both shoes should wear about the same way. If you have pain in one foot, you should make sure you don't have a fallen arch on that side. There are two good tests you can perform at home to detect this problem. Place your fingertips on a wall that you are directly facing and stand on your tiptoes on one foot. If you can't do it, a fallen arch may be the culprit. Stand with your feet parallel. Have someone stand in back of you and look at your feet from behind. You can also do it yourself if you stand with your back to a mirror. Normally, only the pinky toe is visible from behind. If one foot is flatter than the other, the 4th and sometimes the 3rd toe on that foot can also be seen.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
There are different modalities of treatment that are available to manage flat feet and fallen arches. The type of treatment that is chosen depends upon how severe the condition is and what symptoms the patients are experiencing. Below is a brief description of the available treatment modalities. In the event that the patient is experiencing swelling of the feet, rest and ice application is usually the initial treatment step. Oral anti-inflammatories may be offered which can help reduce inflammation as well as associated pain. Physical therapy has good outcomes and can include different exercises such as stretches and strengthening of the surrounding muscles. Changes in footwear and activity modification are also important when dealing with a painful flat (pronated) foot. These days, orthotic insoles are easily available either over the counter or through your Podiatrist which can effectively help maintain the arch of the foot and reduce the amount of stress placed on the foot. Podiatrists are able to prescribe a variety of different devices from prefabricated to customized and are trained to determine the most appropriate device for each individual. In order to offer the right kind of orthotic insole, podiatrists may perform a test called gait analysis. This involves asking the patient to walk and videoing the different movements that the foot of forms during the walking. Features such as over pronation can be easily seen on this and orthotic insoles can be prescribed to correct the specific abnormalities that are picked up on this analysis. Overall, orthotic treatment can result in a significant improvement in foot movement and reduction in foot discomfort.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).

There are two types of flatfeet. Flexible flatfoot means that the foot has some arch, even if it only appears when the person flexes the feet or stands on the toes. This is a normal condition that is generally painless and does not require treatment. Stiff, inflexible, or painful flatfoot is an abnormal condition and may indicate a bone abnormality in the foot, a disease, or an injury. Flatfeet are a normal condition in infants and toddlers. This is partly the result of fatty deposits along the bottom of the foot that go away as the child grows. It is also because the ligaments in the foot have not fully developed. Flat-footedness in children is generally painless and does not interfere with walking or activity. In fact, as children learn to walk, the soft tissues in the foot tighten and form the arch. Most children develop arches by late childhood. When flatfeet continue into adulthood, most cases are considered normal. Incidence of flatfeet in the general population is unknown.
Causes
There are many reasons why flat feet develop. Here?s a look at some of the most common causes. Genetics, weak arches, injury, arthritis, diabetes, age, wear and tear on feet, tibialis posterior (ruptured tendon). Nervous system or muscle diseases such as cerebral palsy. Weakness and tightness of other muscles and tendons higher up in the lower extremity. The way our arches form depends on several factors. Our feet are complex structures that comprise twenty-six bones, thirty-three joints, and more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments each. Each foot forms two arches. The arch that runs from the heel to the toe is known as the longitudinal arch, while the one that runs the width is known as the transverse arch. Ligaments (fibrous tissues) give our arches their shape and hold our bones together. The plantar fascia (the long, strong band of connective tissue that runs along the sole of your foot) and muscles add secondary support. There are also foot pads that absorb impact and assist with weight-bearing functions. How these things intertwine and work together determines the formation of our arches. A structural abnormality or injury to one of these components can result in flatfoot.
Symptoms
It?s possible to have fallen arches and experience no symptoms whatsoever. But many people do notice some problems with this condition. Their feet, back and legs ache. Standing on their toes is difficult, if not impossible, and they note swelling around the arch and heel.
Diagnosis
It is important for people with foot pain to know if they have flat feet. The following tests can help you determine your arch type. When you get out of a swimming pool, look at your footprint on the concrete. The front of the foot will be joined to the heel by a strip. If your foot is flat, then the strip is the same width as the front of the foot, creating a footprint that looks like a stretched out pancake. With a normal arch, the strip is about half the width of the front of the foot. If you have a high arch, only a thin strip connects the front of the foot with the heel. Put your shoes on a flat table and view them at eye level from behind. See if the sole is worn evenly. A flat foot will cause more wear on the inside of the sole, especially in the heel area. The shoe will easily rock side to side. A flat foot will also cause the upper part of the shoe to lean inward over the sole. Both shoes should wear about the same way. If you have pain in one foot, you should make sure you don't have a fallen arch on that side. There are two good tests you can perform at home to detect this problem. Place your fingertips on a wall that you are directly facing and stand on your tiptoes on one foot. If you can't do it, a fallen arch may be the culprit. Stand with your feet parallel. Have someone stand in back of you and look at your feet from behind. You can also do it yourself if you stand with your back to a mirror. Normally, only the pinky toe is visible from behind. If one foot is flatter than the other, the 4th and sometimes the 3rd toe on that foot can also be seen.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
There are different modalities of treatment that are available to manage flat feet and fallen arches. The type of treatment that is chosen depends upon how severe the condition is and what symptoms the patients are experiencing. Below is a brief description of the available treatment modalities. In the event that the patient is experiencing swelling of the feet, rest and ice application is usually the initial treatment step. Oral anti-inflammatories may be offered which can help reduce inflammation as well as associated pain. Physical therapy has good outcomes and can include different exercises such as stretches and strengthening of the surrounding muscles. Changes in footwear and activity modification are also important when dealing with a painful flat (pronated) foot. These days, orthotic insoles are easily available either over the counter or through your Podiatrist which can effectively help maintain the arch of the foot and reduce the amount of stress placed on the foot. Podiatrists are able to prescribe a variety of different devices from prefabricated to customized and are trained to determine the most appropriate device for each individual. In order to offer the right kind of orthotic insole, podiatrists may perform a test called gait analysis. This involves asking the patient to walk and videoing the different movements that the foot of forms during the walking. Features such as over pronation can be easily seen on this and orthotic insoles can be prescribed to correct the specific abnormalities that are picked up on this analysis. Overall, orthotic treatment can result in a significant improvement in foot movement and reduction in foot discomfort.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
Heel Discomfort All The Things You Will Need To Know Heel Serious Pain
Overview
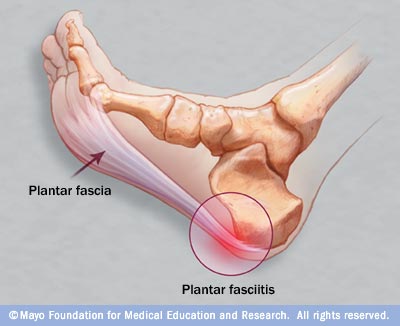
Heel pain is most often caused by plantar fasciitis, a condition that is sometimes also called heel spur syndrome when a spur is present. Heel pain may also be due to other causes, such as a stress fracture, tendonitis, arthritis, nerve irritation, or rarely, a cyst. Because there are several potential causes, it is important to have heel pain properly diagnosed. A foot and ankle surgeon is able to distinguish between all the possibilities and determine the underlying source of your heel pain.
Causes
The most common local causes of heel pain include. Plantar fasciitis, plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the plantar fascia, a fibrous band of tissue on the sole of the foot that helps to support the arch. Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia is overloaded or overstretched. This causes small tears in the fibers of the fascia, especially where the fascia meets the heel bone. Plantar fasciitis may develop in just about anyone but it is particularly common in the following groups of people: people with diabetes, obese people, pregnant women, runners, volleyball players, tennis players and people who participate in step aerobics or stair climbing. You also can trigger plantar fasciitis by pushing a large appliance or piece of furniture or by wearing worn out or poorly constructed shoes. In athletes, plantar fasciitis may follow a period of intense training, especially in runners who push themselves to run longer distances. People with flat feet have a higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis. Heel spur, a heel spur is an abnormal growth of bone at the area where the plantar fascia attaches to the heel bone. It is caused by long-term strain on the plantar fascia and muscles of the foot, especially in obese people, runners or joggers. As in plantar fasciitis, shoes that are worn out, poorly fitting or poorly constructed can aggravate the problem. Heel spurs may not be the cause of heel pain even when seen on an X-ray. In fact, they may develop as a reaction to plantar fasciitis. Calcaneal apophysitis, in this condition, the center of the heel bone becomes irritated as a result of a new shoe or increased athletic activity. This pain occurs in the back of the heel, not the bottom. Calcaneal apophysitis is a fairly common cause of heel pain in active, growing children between the ages of 8 and 14. Although almost any boy or girl can be affected, children who participate in sports that require a lot of jumping have the highest risk of developing this condition. Bursitis means inflammation of a bursa, a sac that lines many joints and allows tendons and muscles to move easily when the joint is moving. In the heel, bursitis may cause pain at the underside or back of the heel. In some cases, heel bursitis is related to structural problems of the foot that cause an abnormal gait (way of walking). In other cases, wearing shoes with poorly cushioned heels can trigger bursitis. Pump bump, this condition, medically known as posterior calcaneal exostosis, is an abnormal bony growth at the back of the heel. It is especially common in young women, in whom it is often related to long-term bursitis caused by pressure from pump shoes. Like other parts of the foot, the heel can be bumped and bruised accidentally. Typically, this happens as a "stone bruise," an impact injury caused by stepping on a sharp object while walking barefoot. In most cases, Achilles tendonitis (inflammation of the Achilles tendon) is triggered by overuse, especially by excessive jumping during sports. However, it also can be related to poorly fitting shoes if the upper back portion of a shoe digs into the Achilles tendon at the back of the heel. Less often, it is caused by an inflammatory illness, such as ankylosing spondylitis (also called axial spondylarthritis), reactive arthritis, gout or rheumatoid arthritis. Compression of a small nerve (a branch of the lateral plantar nerve) can cause pain, numbness or tingling in the heel area. In many cases, this nerve compression is related to a sprain, fracture or varicose (swollen) vein near the heel.
Symptoms
Common symptoms, heel Spurs: the pain is usually worst on standing, particularly first thing in the morning when you get up. It is relatively common, though usually occurring in the over forty's age group. There are no visible features on the heel but a deep localised painful spot can be found in or around the middle of the sole of the heel. Although it is often associated with a spur of bone sticking out of the heel bone (heel spur syndrome), approximately ten per cent of the population have heel spurs without any pain. Heel Bursitis, pain can be felt at the back of the heel when the ankle joint is moved and there may be a swelling on both sides of the Achilles tendon. Or you may feel pain deep inside the heel when it makes contact with the ground. Heel Bumps, recognised as firm bumps on the back of the heel , they are often rubbed by shoes causing pain.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
Home care, in cases that are not severe, home care is probably enough to get rid of heel pain. Rest, avoid running or standing for long periods, or walking on hard surfaces. Avoid activities that may stress the heels. Ice, place an ice-pack on the affected area for about 15 minutes. Do not place bare ice directly onto skin. Footwear. proper-fitting shoes that provide good support are crucial. Athletes should be particularly fussy about the shoes they use when practicing or competing - sports shoes need to be replaced at specific intervals (ask your trainer). Foot supports, wedges and heel cups can help relieve symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
heel pads shoes too big
Prevention

Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.

Heel pain is most often caused by plantar fasciitis, a condition that is sometimes also called heel spur syndrome when a spur is present. Heel pain may also be due to other causes, such as a stress fracture, tendonitis, arthritis, nerve irritation, or rarely, a cyst. Because there are several potential causes, it is important to have heel pain properly diagnosed. A foot and ankle surgeon is able to distinguish between all the possibilities and determine the underlying source of your heel pain.
Causes
The most common local causes of heel pain include. Plantar fasciitis, plantar fasciitis is a painful inflammation of the plantar fascia, a fibrous band of tissue on the sole of the foot that helps to support the arch. Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia is overloaded or overstretched. This causes small tears in the fibers of the fascia, especially where the fascia meets the heel bone. Plantar fasciitis may develop in just about anyone but it is particularly common in the following groups of people: people with diabetes, obese people, pregnant women, runners, volleyball players, tennis players and people who participate in step aerobics or stair climbing. You also can trigger plantar fasciitis by pushing a large appliance or piece of furniture or by wearing worn out or poorly constructed shoes. In athletes, plantar fasciitis may follow a period of intense training, especially in runners who push themselves to run longer distances. People with flat feet have a higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis. Heel spur, a heel spur is an abnormal growth of bone at the area where the plantar fascia attaches to the heel bone. It is caused by long-term strain on the plantar fascia and muscles of the foot, especially in obese people, runners or joggers. As in plantar fasciitis, shoes that are worn out, poorly fitting or poorly constructed can aggravate the problem. Heel spurs may not be the cause of heel pain even when seen on an X-ray. In fact, they may develop as a reaction to plantar fasciitis. Calcaneal apophysitis, in this condition, the center of the heel bone becomes irritated as a result of a new shoe or increased athletic activity. This pain occurs in the back of the heel, not the bottom. Calcaneal apophysitis is a fairly common cause of heel pain in active, growing children between the ages of 8 and 14. Although almost any boy or girl can be affected, children who participate in sports that require a lot of jumping have the highest risk of developing this condition. Bursitis means inflammation of a bursa, a sac that lines many joints and allows tendons and muscles to move easily when the joint is moving. In the heel, bursitis may cause pain at the underside or back of the heel. In some cases, heel bursitis is related to structural problems of the foot that cause an abnormal gait (way of walking). In other cases, wearing shoes with poorly cushioned heels can trigger bursitis. Pump bump, this condition, medically known as posterior calcaneal exostosis, is an abnormal bony growth at the back of the heel. It is especially common in young women, in whom it is often related to long-term bursitis caused by pressure from pump shoes. Like other parts of the foot, the heel can be bumped and bruised accidentally. Typically, this happens as a "stone bruise," an impact injury caused by stepping on a sharp object while walking barefoot. In most cases, Achilles tendonitis (inflammation of the Achilles tendon) is triggered by overuse, especially by excessive jumping during sports. However, it also can be related to poorly fitting shoes if the upper back portion of a shoe digs into the Achilles tendon at the back of the heel. Less often, it is caused by an inflammatory illness, such as ankylosing spondylitis (also called axial spondylarthritis), reactive arthritis, gout or rheumatoid arthritis. Compression of a small nerve (a branch of the lateral plantar nerve) can cause pain, numbness or tingling in the heel area. In many cases, this nerve compression is related to a sprain, fracture or varicose (swollen) vein near the heel.
Symptoms
Common symptoms, heel Spurs: the pain is usually worst on standing, particularly first thing in the morning when you get up. It is relatively common, though usually occurring in the over forty's age group. There are no visible features on the heel but a deep localised painful spot can be found in or around the middle of the sole of the heel. Although it is often associated with a spur of bone sticking out of the heel bone (heel spur syndrome), approximately ten per cent of the population have heel spurs without any pain. Heel Bursitis, pain can be felt at the back of the heel when the ankle joint is moved and there may be a swelling on both sides of the Achilles tendon. Or you may feel pain deep inside the heel when it makes contact with the ground. Heel Bumps, recognised as firm bumps on the back of the heel , they are often rubbed by shoes causing pain.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is generally made during the history and physical examination. There are several conditions that can cause heel pain, and plantar fasciitis must be distinguished from these conditions. Pain can be referred to the heel and foot from other areas of the body such as the low back, hip, knee, and/or ankle. Special tests to challenge these areas are performed to help confirm the problem is truly coming from the plantar fascia. An X-ray may be ordered to rule out a stress fracture of the heel bone and to see if a bone spur is present that is large enough to cause problems. Other helpful imaging studies include bone scans, MRI, and ultrasound. Ultrasonographic exam may be favored as it is quick, less expensive, and does not expose you to radiation. Laboratory investigation may be necessary in some cases to rule out a systemic illness causing the heel pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter's syndrome, or ankylosing spondylitis. These are diseases that affect the entire body but may show up at first as pain in the heel.
Non Surgical Treatment
Home care, in cases that are not severe, home care is probably enough to get rid of heel pain. Rest, avoid running or standing for long periods, or walking on hard surfaces. Avoid activities that may stress the heels. Ice, place an ice-pack on the affected area for about 15 minutes. Do not place bare ice directly onto skin. Footwear. proper-fitting shoes that provide good support are crucial. Athletes should be particularly fussy about the shoes they use when practicing or competing - sports shoes need to be replaced at specific intervals (ask your trainer). Foot supports, wedges and heel cups can help relieve symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
heel pads shoes too big
Prevention

Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.
Treating Mortons Neuroma
Overview
 Put simply - Morton's neuroma is a swollen (inflamed) nerve in the ball of the foot, commonly between the base of the second and third toes. Patients experience numbness and pain in the affected area, which is relieved by removing footwear and/or massaging the foot. A neuroma is a tumor that arises in nerve cells, a benign growth of nerve tissue that can develop in various parts of the body. In Morton's neuroma the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes thickens, causing a sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot. A sharp severe pain, often described as a red hot needle may come on suddenly while walking. There may also be numbness, burning and stinging in the toes. Although it is labeled a neuroma, many say it is not a true tumor, but rather a perineural fibroma (fibrous tissue formation around nerve tissue).
Put simply - Morton's neuroma is a swollen (inflamed) nerve in the ball of the foot, commonly between the base of the second and third toes. Patients experience numbness and pain in the affected area, which is relieved by removing footwear and/or massaging the foot. A neuroma is a tumor that arises in nerve cells, a benign growth of nerve tissue that can develop in various parts of the body. In Morton's neuroma the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes thickens, causing a sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot. A sharp severe pain, often described as a red hot needle may come on suddenly while walking. There may also be numbness, burning and stinging in the toes. Although it is labeled a neuroma, many say it is not a true tumor, but rather a perineural fibroma (fibrous tissue formation around nerve tissue).
Causes
In many cases, a neuroma may develop as a result of excessive loading on the front of the foot. Sometimes, a patient?s anatomic alignment in the forefoot contributes to the overload. There may be some cases where the neuroma develops spontaneously, for no obvious reason. However, once the nerve is irritated, pressure from walking, and from the adjacent bony prominences (metatarsal heads), as well as from the intermetatarsal ligament that binds the heads together, all may contribute to persistent pain. Repetitive pressure on the nerve causes localized injury with resulting scarring and fibrosis of the nerve. This leads to symptoms in the distribution of the nerve.
Symptoms
Symptoms include: pain on weight bearing, frequently after only a short time. The nature of the pain varies widely among individuals. Some people experience shooting pain affecting the contiguous halves of two toes. Others describe a feeling like having a pebble in their shoe or walking on razor blades. Burning, numbness, and paresthesia may also be experienced. Morton's neuroma lesions have been found using MRI in patients without symptoms.
Diagnosis
The doctor will perform an examination of your feet as well. He or she may palpate your feet and flex them in specific ways that will indicate the presence of a neuroma. X-rays are often used to rule out other problems, such as fractures, bone spurs, arthritis or other problems with the bones in the toes or foot. In some cases, an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be helpful to confirm the presence of a neuroma.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wear shoes with plenty of room for the toes to move, low heels, and laces or buckles that allow for width adjustment. Wear shoes with thick, shock-absorbent soles, as well as proper insoles that are designed to keep excessive pressure off of the foot. High-heeled shoes over two inches tall should be avoided whenever possible because they place undue strain on the forefoot. Resting the foot and massaging the affected area can temporarily alleviate neuroma pain. Use an ice pack to help to dull the pain and improve comfort. Use over-the-counter shoe pads. These pads can relieve pressure around the affected area.
Surgical Treatment
For severe or persistent pain, you may need surgery to remove the neuroma. Once the nerve is gone, you permanently lose feeling in the affected area. One alternative to surgery is to undergo neurolysis injections. These use chemical agents to block pain signals. Another alternative is to take a prescription pain reliever that alleviates nerve pain.
 Put simply - Morton's neuroma is a swollen (inflamed) nerve in the ball of the foot, commonly between the base of the second and third toes. Patients experience numbness and pain in the affected area, which is relieved by removing footwear and/or massaging the foot. A neuroma is a tumor that arises in nerve cells, a benign growth of nerve tissue that can develop in various parts of the body. In Morton's neuroma the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes thickens, causing a sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot. A sharp severe pain, often described as a red hot needle may come on suddenly while walking. There may also be numbness, burning and stinging in the toes. Although it is labeled a neuroma, many say it is not a true tumor, but rather a perineural fibroma (fibrous tissue formation around nerve tissue).
Put simply - Morton's neuroma is a swollen (inflamed) nerve in the ball of the foot, commonly between the base of the second and third toes. Patients experience numbness and pain in the affected area, which is relieved by removing footwear and/or massaging the foot. A neuroma is a tumor that arises in nerve cells, a benign growth of nerve tissue that can develop in various parts of the body. In Morton's neuroma the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes thickens, causing a sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot. A sharp severe pain, often described as a red hot needle may come on suddenly while walking. There may also be numbness, burning and stinging in the toes. Although it is labeled a neuroma, many say it is not a true tumor, but rather a perineural fibroma (fibrous tissue formation around nerve tissue).Causes
In many cases, a neuroma may develop as a result of excessive loading on the front of the foot. Sometimes, a patient?s anatomic alignment in the forefoot contributes to the overload. There may be some cases where the neuroma develops spontaneously, for no obvious reason. However, once the nerve is irritated, pressure from walking, and from the adjacent bony prominences (metatarsal heads), as well as from the intermetatarsal ligament that binds the heads together, all may contribute to persistent pain. Repetitive pressure on the nerve causes localized injury with resulting scarring and fibrosis of the nerve. This leads to symptoms in the distribution of the nerve.
Symptoms
Symptoms include: pain on weight bearing, frequently after only a short time. The nature of the pain varies widely among individuals. Some people experience shooting pain affecting the contiguous halves of two toes. Others describe a feeling like having a pebble in their shoe or walking on razor blades. Burning, numbness, and paresthesia may also be experienced. Morton's neuroma lesions have been found using MRI in patients without symptoms.
Diagnosis
The doctor will perform an examination of your feet as well. He or she may palpate your feet and flex them in specific ways that will indicate the presence of a neuroma. X-rays are often used to rule out other problems, such as fractures, bone spurs, arthritis or other problems with the bones in the toes or foot. In some cases, an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be helpful to confirm the presence of a neuroma.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wear shoes with plenty of room for the toes to move, low heels, and laces or buckles that allow for width adjustment. Wear shoes with thick, shock-absorbent soles, as well as proper insoles that are designed to keep excessive pressure off of the foot. High-heeled shoes over two inches tall should be avoided whenever possible because they place undue strain on the forefoot. Resting the foot and massaging the affected area can temporarily alleviate neuroma pain. Use an ice pack to help to dull the pain and improve comfort. Use over-the-counter shoe pads. These pads can relieve pressure around the affected area.

Surgical Treatment
For severe or persistent pain, you may need surgery to remove the neuroma. Once the nerve is gone, you permanently lose feeling in the affected area. One alternative to surgery is to undergo neurolysis injections. These use chemical agents to block pain signals. Another alternative is to take a prescription pain reliever that alleviates nerve pain.
Shoe Lifts The Podiatrists Answer For Leg Length Imbalances
There are actually two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital means that you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. As a result of developmental periods of aging, the human brain senses the gait pattern and recognizes some variation. The human body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch is not blatantly abnormal, does not need Shoe Lifts to compensate and mostly won't have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiscovered on a daily basis, however this condition is very easily remedied, and can eliminate a number of instances of lumbar pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality usually involves Shoe Lifts. These are cost-effective, often being under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or higher. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most common condition impacting people today. Around 80 million people suffer from back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs companies vast amounts of money each year because of lost time and productivity. New and improved treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of minimizing the economic impact this issue causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In these types of situations Shoe Lifts can be of very useful. The lifts are capable of decreasing any discomfort and pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless professional orthopaedic practitioners".
In order to support the human body in a healthy and balanced manner, feet have got a critical job to play. In spite of that, it's often the most overlooked region in the human body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there is unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that ideal posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiscovered on a daily basis, however this condition is very easily remedied, and can eliminate a number of instances of lumbar pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality usually involves Shoe Lifts. These are cost-effective, often being under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or higher. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most common condition impacting people today. Around 80 million people suffer from back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs companies vast amounts of money each year because of lost time and productivity. New and improved treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of minimizing the economic impact this issue causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In these types of situations Shoe Lifts can be of very useful. The lifts are capable of decreasing any discomfort and pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless professional orthopaedic practitioners".
In order to support the human body in a healthy and balanced manner, feet have got a critical job to play. In spite of that, it's often the most overlooked region in the human body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there is unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that ideal posture and balance are restored.
Controlling Heel Spur

Overview
Heel spurs, pointed, bony outgrowths of the heel, are caused by localized soft tissue inflammation and can be located at the back of the heel or under the heel, beneath the sole of the foot. Plantar fascitis is associated with inflammation caused by heel spurs on the soles of the feet. Both conditions are treated with ice application and anti-inflammatory medications. Orthotics may also provide some relief.
Causes
Heel spurs under the sole of the foot (plantar area) are associated with inflammation of the plantar fascia (fasciitis), the "bowstring-like" tissue stretching underneath the sole that attaches at the heel. Plantar heel spurs cause localized tenderness and pain made worse when stepping down on the heel. Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis can occur alone or be related to underlying diseases that cause arthritis (inflammation of the joints), such as reactive arthritis (formerly called Reiter's disease), ankylosing spondylitis, and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. It is important to note that heel spurs may cause no symptoms at all and may be incidentally discovered during X-ray exams taken for other purposes.
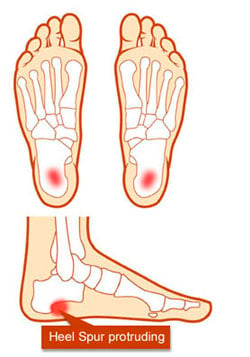
Symptoms
Heel spurs often do not show any symptoms. If you have intermittent or chronic pain when you walk, run or jog, it may be heel spur. There will be inflammation the point where spur formation happens. The pain is caused by soft tissue injury in the heel. Patients often describe the pain as a pin or knife sticking to the heel. The pain is more specially in the morning when the patient stands up for the first time.
Diagnosis
Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your heel spur or plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to heel spurs and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays will show calcification or bone within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus. This is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter or prescription-strength anti-inflammatory medications can help temporarily, but can cause side effects with prolonged use - the most significant being gastrointestinal upset, ulceration and bleeding. Deep tissue massage, taping and other physical therapy modalities can also be helpful. Arch support is highly recommended, either with shoe inserts or custom orthotics made by podiatrists. If pain continues, a steroid injection at the site of pain may be recommended; however, many physicians do not like injecting around the heel. The side effects of steroids injected in this area can be serious and worsen symptoms. Complications can include fat necrosis (death of fatty tissue) of the heel and rupture of the plantar fascia.
Surgical Treatment
Most studies indicate that 95% of those afflicted with heel spurs are able to relieve their heel pain with nonsurgical treatments. If you are one of the few people whose symptoms don?t improve with other treatments, your doctor may recommend plantar fascia release surgery. Plantar fascia release involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament in order to release the tension and relieve the inflammation of the ligament. Sometimes the bone spur is also removed, if there is a large spur (remember that the bone spur is rarely a cause of pain. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with heel spurs. One should always be sure to understand all the risks associated with any surgery they are considering.
Prevention
Walk around before you buy shoes. Before you purchase your shoes, do the following. Re-lace the shoes if you're trying on athletic shoes. Start at the farthest eyelets and apply even pressure to the laces as you come closer to the tongue of the shoe. Make sure that you can wiggle your toes freely inside of the shoe. Also, make sure that you have at enough space between your tallest toe and the end of the shoe. You should have room equal to about the width of your thumb in the tip of your shoe. Walk around to make sure that the shoe has a firm grip on your heel without sliding up and down. Walk or run a few steps to make sure your shoes are comfortable. Shoes that fit properly require no break-in period.
Just What Is Inferior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
A heel spur is a calcium deposit causing a bony protrusion on the underside of the heel bone. On an X-ray, a heel spur can extend forward by as much as a half-inch. Without visible X-ray evidence, the condition is sometimes known as "heel spur syndrome." Although heel spurs are often painless, they can cause heel pain. They are frequently associated with plantar fasciitis, a painful inflammation of the fibrous band of connective tissue (plantar fascia) that runs along the bottom of the foot and connects the heel bone to the ball of the foot. Treatments for heel spurs and associated conditions include exercise, custom-made orthotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and cortisone injections. If conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary.
Causes
Athletes who participate in sports that involve a significant amount of jumping and running on hard surfaces are most likely to suffer from heel spurs. Some other risk factors include poor form while walking which can lead to undue stress on the heel and its nerves and ligaments. Shoes that are not properly fitted for the wearer?s feet. Poor arch support in footwear. Being overweight. Occupations that require a lot of standing or walking. Reduced flexibility and the thinning of the fat pad along the bottom of the heel, both of which are a typical depreciation that comes with aging.

Symptoms
If your body has created calcium build-ups in an effort to support your plantar fascia ligament, each time you step down with your foot, the heel spur is being driven into the soft, fatty tissue which lines the bottom of your heel. Heel spur sufferers experience stabbing sensations because the hard protrusion is literally being jabbed into the heel pad. If left untreated, Plantar Fasciitis and heel spurs can erode the fatty pad of the heel and cause permanent damage to the foot. Fortunately, most cases can be resolved without medications or surgeries.
Diagnosis
Most patients who are suffering with heel spurs can see them with an X-ray scan. They are normally hooked and extend into the heel. Some people who have heel spur may not even have noticeable symptoms, although could still be able to see a spur in an X-ray scan.
Non Surgical Treatment
The majority of heel spurs are treated with non-surgical interventions. These can relieve pain, but may take from about 3 months to up to a year for symptoms to resolve. Rest, icing, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory or prescription medications can help ease symptoms. Cortisone injections may also be used. Physical therapists may instruct you to perform stretching exercises to help relax the tissues in the heel. Your doctor may recommend custom orthotics or shoe inserts to position and cushion your heel. Night splints can help position the heel and arch of the foot while you sleep. Some doctors may recommend extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT). This treatment uses energy pulses to start the repair process in the heel tissues. ESWT is recommend when other non-surgical treatments have failed.
Surgical Treatment
Sometimes bone spurs can be surgically removed or an operation to loosen the fascia, called a plantar fascia release can be performed. This surgery is about 80 percent effective in the small group of individuals who do not have relief with conservative treatment, but symptoms may return if preventative measures (wearing proper footwear, shoe inserts, stretching, etc) are not maintained.
Bursa Foot Surgery Rehabilitation
Overview
A lesser known type of heel pain is a condition called Bursitis of the Heel. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that cushions the muscles, tendons and bones in our joints. It helps keep them from rubbing against each other and reduces friction in the areas around the joints. Bursitis is Latin for inflammation of the bursa. Repeated movement and pressure on the bursa can cause it to swell and become inflamed. Trauma, infection or crystal deposits can also cause Bursitis. The joints that are usually affected by bursitis are the large joints such as the shoulder, hip and knee but in some cases also the back of the heel.
Causes
Bursitis has many causes, including autoimmune disorders, crystal deposition (gout and pseudogout), infectious diseases, traumatic events, and hemorrhagic disorders, as well as being secondary to overuse. Repetitive injury within the bursa results in local vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability, which stimulate the inflammatory cascade.
Symptoms
In retrocalcaneal bursitis, pain at the back of the heel is the main complaint from patients. Pain may worsen when tip-toeing, running uphill, jumping or hopping. Often, those who are accustomed to wearing high-heeled shoes on a long-term basis may also complain of pain at the back of the heel when switching to flat shoes. This is because when in high-heeled shoes, the calf muscle and the Achilles tendon are in a shortened position. Switching to flat shoes would cause an increased stretch to the calf muscle and Achilles tendon, irritating the Achilles tendon and the retrocalcaneal bursa. Other symptoms may include redness and swelling at the back of the heel.
Diagnosis
Medical examination is not necessarily required in light cases where the tenderness is minimal. In all cases where smooth improvement is not experienced, medical attention should be sought as soon as possible to exclude a (partial) rupture of the Achilles tendon or rupture of the soleus muscle. This situation is best determined by use of ultrasound scanning, as a number of injuries requiring treatment can easily be overlooked during a clinical examination (Ultrasonic image). Ultrasound scanning enables an evaluation of the extent of the change in the tendon, inflammation of the tendon (tendinitis), development of cicatricial tissue (tendinosis), calcification, inflammation of the tissue surrounding the tendon (peritendinitis), inflammation of the bursa (bursitis), as well as (partial) rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
All types of bursitis often can be successfully managed non-surgically, and possible treatments include use of ice packs or compressive dressings, activity modification that may reduce stress or irritation, administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or antibiotics, corticosteroid injections (knee and elbow), stretching exercises, and/or change of footwear (heel). Surgery may be required in patients whose symptoms remain following these treatments and in certain situations when infection is involved.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely need to treat most of these conditions. A patient with a soft tissue rheumatic syndrome may need surgery, however, if problems persist and other treatment methods do not help symptoms.
Prevention
People can lower the risk of bursitis by gradually strengthening and stretching the muscles around the joints and taking regular breaks from repetitive motion that might irritate bursae. Prolonged time resting on the elbows or kneeling should be avoided, if it cannot be avoided, wearing cushioned elbow and knee pads can help protect the bursae. Comfortable, supportive, low-heeled shoes can help prevent bursitis in the foot.
A lesser known type of heel pain is a condition called Bursitis of the Heel. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that cushions the muscles, tendons and bones in our joints. It helps keep them from rubbing against each other and reduces friction in the areas around the joints. Bursitis is Latin for inflammation of the bursa. Repeated movement and pressure on the bursa can cause it to swell and become inflamed. Trauma, infection or crystal deposits can also cause Bursitis. The joints that are usually affected by bursitis are the large joints such as the shoulder, hip and knee but in some cases also the back of the heel.
Causes
Bursitis has many causes, including autoimmune disorders, crystal deposition (gout and pseudogout), infectious diseases, traumatic events, and hemorrhagic disorders, as well as being secondary to overuse. Repetitive injury within the bursa results in local vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability, which stimulate the inflammatory cascade.
Symptoms
In retrocalcaneal bursitis, pain at the back of the heel is the main complaint from patients. Pain may worsen when tip-toeing, running uphill, jumping or hopping. Often, those who are accustomed to wearing high-heeled shoes on a long-term basis may also complain of pain at the back of the heel when switching to flat shoes. This is because when in high-heeled shoes, the calf muscle and the Achilles tendon are in a shortened position. Switching to flat shoes would cause an increased stretch to the calf muscle and Achilles tendon, irritating the Achilles tendon and the retrocalcaneal bursa. Other symptoms may include redness and swelling at the back of the heel.
Diagnosis
Medical examination is not necessarily required in light cases where the tenderness is minimal. In all cases where smooth improvement is not experienced, medical attention should be sought as soon as possible to exclude a (partial) rupture of the Achilles tendon or rupture of the soleus muscle. This situation is best determined by use of ultrasound scanning, as a number of injuries requiring treatment can easily be overlooked during a clinical examination (Ultrasonic image). Ultrasound scanning enables an evaluation of the extent of the change in the tendon, inflammation of the tendon (tendinitis), development of cicatricial tissue (tendinosis), calcification, inflammation of the tissue surrounding the tendon (peritendinitis), inflammation of the bursa (bursitis), as well as (partial) rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
All types of bursitis often can be successfully managed non-surgically, and possible treatments include use of ice packs or compressive dressings, activity modification that may reduce stress or irritation, administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or antibiotics, corticosteroid injections (knee and elbow), stretching exercises, and/or change of footwear (heel). Surgery may be required in patients whose symptoms remain following these treatments and in certain situations when infection is involved.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely need to treat most of these conditions. A patient with a soft tissue rheumatic syndrome may need surgery, however, if problems persist and other treatment methods do not help symptoms.
Prevention
People can lower the risk of bursitis by gradually strengthening and stretching the muscles around the joints and taking regular breaks from repetitive motion that might irritate bursae. Prolonged time resting on the elbows or kneeling should be avoided, if it cannot be avoided, wearing cushioned elbow and knee pads can help protect the bursae. Comfortable, supportive, low-heeled shoes can help prevent bursitis in the foot.